Don't fall for the bait
We care about your cybersecurity. You should too.
Did you know 91% of successful hacks and data breaches start with phishing scams?
Phishing: What is it?
Phishing is a cybercrime with the intent to acquire sensitive data such as personally identifiable information, banking and credit card details, passwords, and more. This process is done by targeting an individual or group and pretending to be a trustworthy source via email.
It might be a fraudulent email from an IT administrator, popular social media site, bank, or even an employee with whom you are close. This is criminal behavior, and you must keep a watchful eye for it.
6 Common Phishing Methods
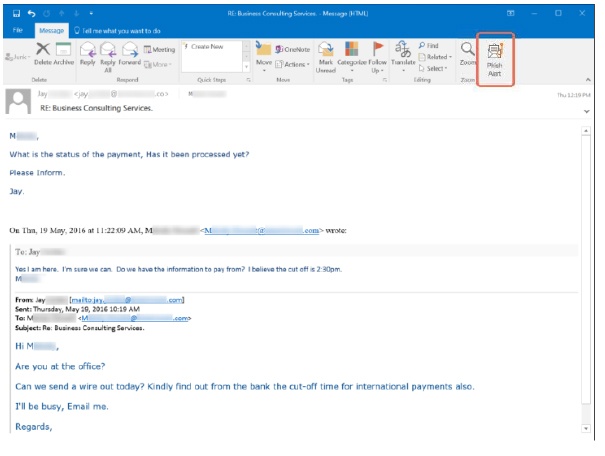
1. Spear Phishing
Though similar to a classic phishing attack, spear phishing is more targeted. Whereas phishing goes after a large group of people to see what sticks, spear phishing is highly targeted and requires advanced hacking methods. Spear phishing aims to get more than just credit card data. It goes for more valuable confidential information, even business secrets, and typically attempts to gain access to the larger network rather than a one-and-done attack.
2. Email/Spam
Perhaps one of the most common techniques used, this attack will come in the form of an email sent to hundreds, thousands, even millions of users with a request for personal details. These emails will typically prompt the user to act urgently, and the details provided can be used to access banking or credit card information. The user may be asked to fill out a form in the process or access a suspicious link.
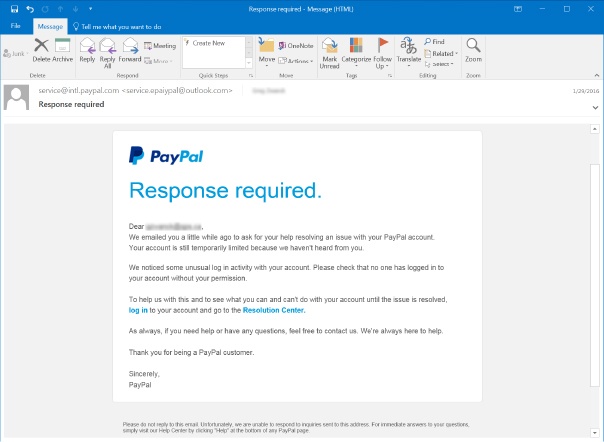
3. Smishing (SMS Phishing)
This is phishing done via Short Message Services (SMS) and typically occurs on a cell phone. This method has become a very common type of spear phishing. Smishing attempts will pretend to be a seemingly trustworthy source such as number claiming to be from the IRS or an invoice for something you supposedly ordered. This text will attempt to entice the user to reveal personal information via a link that leads to a phishing site.
4. Vishing (Voice Phishing)
Voice Phishing is primarily done using a fake caller ID, will target the user via cell phone, and prompt them to dial another number. The attacker will then attempt to get personal information such as a bank account number over the phone. This can be a useful method for hackers as the user doesn’t have much time to react to what is going on in real time.
5. Website Forgery
These are fake websites built by hackers that are either made to look like a legitimate independent website or a replica of an already existing one. The goal here is to deceive the user by attaining information that could be used to defraud or launch other attacks on the victim.
6. Malware and Ransomware
Malware is a general term for any programs designed to harm, disrupt, and hack devices. Phishing scams involving malware typically hide themselves within emails and attachments. Clicking on a suspicious link or downloading an untrusted file gives the hacker control of your system. Ransomware is a subcategory of malware, encrypting user data using typical methods such as social engineering, suspicious links, etc. Once the data is accessed by the hacker, it will be held hostage with the demand of a ransom.
There are other types of phishing out there. For a more comprehensive list of phishing techniques and more information on phishing, visit KnowBe4.
Phishing Protection Tips
Here are some things you can do to remain vigilant when it comes to phishing attacks.

Look at the sender’s email address.
Don’t be so quick to reply to an email that seems to be from a trustworthy source or someone you know. Take a close look at the email address. There might be a misspelling or something else unusual that stands out.

Never give out sensitive information.
If you receive a request for private information, verify that the request isn’t a phishing scam. It’s rare that you would be prompted to give any kind of personal information via email and that could be a sign of a phishing attempt.

Think before you click.
Ask yourself, is this link really to a trusted site? Do I even know this person? Why was I sent this? These questions can help you avoid clicking on links that take you to scam websites.

Keep informed about phishing techniques.
New strategies for stealing private information are developed all the time, so it’s important to stay up to date. Check out KnowBe4’s blog for the latest phishing scams and other cybersecurity news.

Call to confirm.
If you’re ever unsure about an email, call, job posting, or application from a sender, contact that sender directly over the phone, not via link or anything else provided in the email.
What is UMA doing to help?
At UMA, we are committed to care. From our team members to students and alumni, we want to make sure the UMA family is safe. And it’s our commitment to technology that allows us to do just that.
Whether it’s the 24/7 tech support for our students or security measures being taken to protect people’s personal information, UMA is committed to providing resources and implementing strategies designed for our tech and cybersecurity needs.